Hi guys, this is Pushan Mohanta and today I am starting my blog with the topic braking system.
Hope you will like it;
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system.It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
Disc Brakes: A friction system using a wheel brake to slow the rotation of the automobiles wheels.
Hope you will like it;
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system.It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
Depending on the vehicle you are driving, there are different types of brake systems.
Mainly there are two types of systems
- Drum Brakes: A friction system using a set of shoes or pads to press against a brake drum.

Drum brakes - There are few more types of braking system
- Single-Circuit Hydraulic Brakes:
- Dual-Circuit Hydraulic Brakes:
- Brake-by-wire:
- Antilock Braking System (ABS):
- Power Brake Booster:
- Air Brakes:
- Advanced Emergency Braking System (AEBS):
- There are three common characteristics of service brake systems that can be found in modern day vehicles, including:
- Friction
- Pumping
- Electromagnetic
Modern braking systems will employ one of these types of brakes. - Before learning about the different types of brakes that make up modern braking systems and the different systems that an automobile can have, its helpful to know some of the parts that comprise a typical automotive braking system.This list includes:
- Brake Pads: steel backing plates used in disk brakes; friction material is bound to the surface facing the rotor and is usually made of ceramic, metal or other hard-wearing composite materials.

brake shoe - Brake Shoes: 2 pieces of sheet steel welded together that carry the brake lining
- Brake Drum: rotating drum-shaped component used in drum brakes
- Brake Lining: heat-resistant, soft but tough material with a high friction characteristic housed inside a brake shoe
- Rotor: cast iron brake disc connected to wheel and/or axle; sometimes made of reinforced carbon-carbon, ceramic matrix or other composite
- Piston: a moving component contained by a cylinder
- Caliper: a device on which brake pads and pistons are mounted
- Floating Calipers: moves relative to rotor; uses a piston on a single side of disc to push inner brake pad into braking surface before pulling caliper body in to apply pressure on opposite side of disc.
- Fixed Calipers: does not move relative to rotor and is sensitive to imperfections; uses one or more single pairs of opposing pistons to clamp from each side of the rotor
- Floating Calipers: moves relative to rotor; uses a piston on a single side of disc to push inner brake pad into braking surface before pulling caliper body in to apply pressure on opposite side of disc.
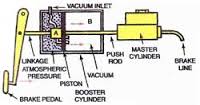
- Master Cylinder: a device that converts the non-hydraulic pressure from your foot into hydraulic pressure and controls slave cylinders at the opposite end of the hydraulic system.
- Vacuum Servo/Brake Booster: a component used to enhance the master cylinder and augment pressure from a drivers foot through the use of a vacuum in the engine intake.
- Guys plz comment if any other topic you want to know








Thank you sir for your valuable information
ReplyDelete